A hard drive is used in computers or laptops to save various forms of data.
When installing a new hard drive or wanting to delete your drive entirely for that “fresh” sensation, formatting your drive will be necessary.
Formatting refers to the procedure of creating a file system on a volume or partition, enabling the operating system to save and access data on it.
A file system provides a method for structuring and accessing information stored on a hard drive or other forms of storage. It comes into existence when the volume is formatted.
However, before diving into the main instructions, let’s first talk about the most typical scenarios where formatting your hard drive is required.
When Do You Need to Format a Hard Drive?
Formatting a hard drive isn’t overly complicated, but doing it correctly is crucial. There are several scenarios where reformatting the hard drive becomes essential.
Let’s take a look at some common scenarios:
- The computer fails to boot: If your computer cannot start or consistently shows a black screen, you may need to format your hard drive.
- The hard drive is nearly full: After years of usage, your internal hard drive can become cluttered. In this case, you’ll require additional space to save more files, and you may choose to format your drive.
- Registry issues: If your computer is experiencing numerous registry problems, formatting the drive could be one solution.
- Reinstalling the operating system: If you are planning to reinstall the OS, you will need to format the C Drive beforehand.
- Modifying the file system: When you need to change your hard drive’s file system, or the file system is incompatible, formatting is required.
- Creating a new partition: When establishing a new partition on your hard drive, you should format it before storing files.
- Virus infection: If your external hard drive has been attacked by a virus, you will need to format it before using it with an uninfected machine.
- External hard drive errors: When you connect your external HDD to the PC, error messages may pop up, like “You need to format the disk in drive X: before you can use it.” Typically, formatting the drive is the best solution to eliminate these error messages.
- Selling your device: If you intend to sell your old computer or laptop, it is necessary to format the hard drive.
No matter your reason for formatting your hard drive, the most important thing you need to take into account is determining which file system you will utilize.
Therefore, let’s explore which file system is the best choice.
What File System Can You Choose While Formatting a Hard Drive?
Operating Systems utilize file systems to save data on storage devices. If you are using Windows, NTFS is a suitable option.
There isn’t a universal file system that all hard drives share, so the file system used is determined by the drive and the Operating System of the computer.
Below, we have included a useful table to provide you with more information about these file systems you may want to consider.
| Windows 11/10 File System | Overview |
| NTFS | This is the default file system used by Windows. It can handle up to 256 TB and allows for files as large as 18 EB. Additionally, it is the sole file system that supports compression, encryption, and permissions. It is the most effective disk format in Windows 11/10 for safeguarding data. |
| FAT32 | FAT32 is an outdated file system that dates back to Windows 95 and works with a wide range of files. However, it cannot accommodate files larger than 4GB. Windows continues to provide support for it. |
| exFAT | exFAT is a widely used format for external storage media like flash drives and solid-state drives since it works well with both Windows and macOS systems. While it is not as commonly used as NTFS, exFAT is a practical choice for plug-and-play functionality. It can support up to 128 PB and individual files as large as 16 EB. |
| ReFS | ReFS (Resilient File System) offers more storage capacity (4.7 ZB volumes and files up to 18 EB). It is available for Windows Server 2012 and later, Windows Enterprise Build 1709 and earlier, and Windows 10/11 Pro. It actively resolves mistakes, recovers data from corruption, verifies the integrity of metadata, and improves performance. However, in contrast to NTFS, it lacks support for file compression and encryption. |
After learning the file system for Windows, you may wonder: Is it possible to format a hard drive without losing data? Keep reading to get the answer.
Can I Format a Hard Drive Without Losing Data?
Yes, it is possible to format a hard drive while preserving your data, but this is only achievable if you follow the correct procedure during the formatting.
Case 1. You don’t format the drive before making a backup.
If you haven’t yet formatted your drive, the first step is to create a complete backup of all essential files.
To back up your external/internal hard drive, we advise using MiniTool ShadowMaker (free for 30 days). It can help back up files, partitions, and disks.
MiniTool ShadowMaker TrialClick to Download100%Clean & Safe
After that, you can proceed to format your drive with your preferred settings and restore your files from the backup.
Case 2. You have formatted your hard drive or want to reformat it.
If your drive has already been formatted and you are looking to recover the data lost due to that, you need to consider the type of formatting that was done:
- Quick Format: In the case of a quick format, there’s still a possibility of retrieving your files using data recovery software. However, the success of the recovery will depend on several aspects, including whether any new data has been written to the drive following the format.
- Full Format: When a full format is carried out, the drive experiences a complete overwriting of all sectors. Regrettably, this indicates that your data is permanently deleted and cannot be recovered, even by specialized data recovery services.
Case 3. You want to change the file system by converting it.
If you wish to change the file system while keeping all files in their current location, for example, moving from FAT32 to NTFS in Windows, this can be accomplished without losing any data by using a specific built-in command to convert the file system.
How to Format a Hard Drive on Windows
If you want to format an external drive on Windows 11/10 or reformat an internal disk, you can utilize any of the methods below to partition it and establish a new file system.
Let’s jump into the specific and hassle-free methods to format a hard drive.
Way 1. From Windows File Explorer
File Explorer offers the simplest method for formatting an HDD on Windows 11/10, as well as any other internal or external storage device. Here’s what to do:
Step 1. Press Win + E to open the File Explorer.
Step 2. Click on This PC. You will view all the drive partitions.
Step 3. Right-click on the partition you wish to format.
Step 4. Choose Format from the options presented.
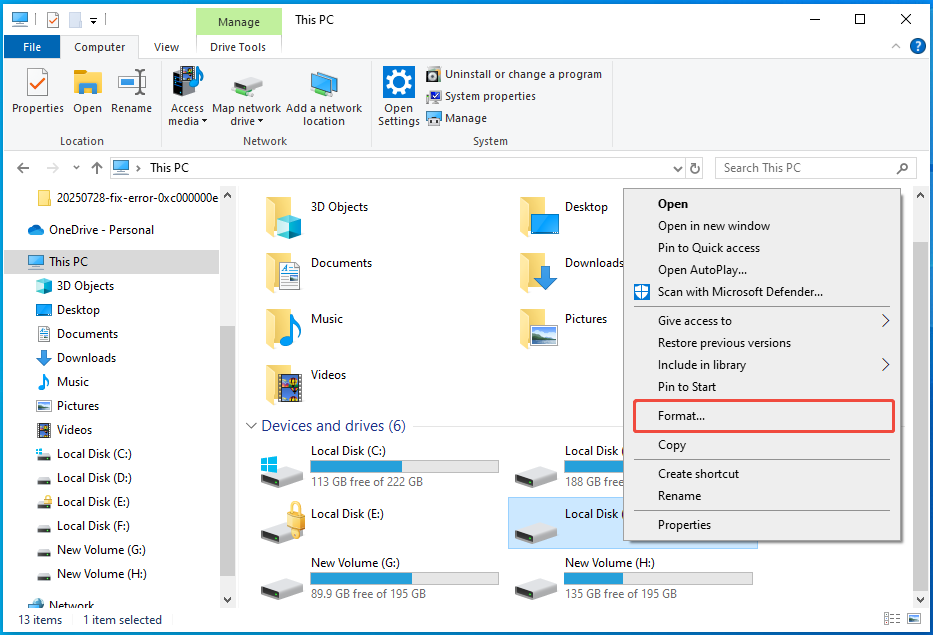
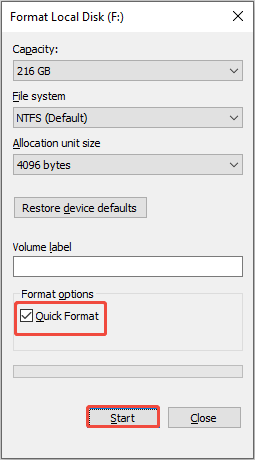
Step 5. Select the file system. If the drive is used within the Windows environment, opt for NTFS. For external drives, choose FAT32 or exFAT.
Step 6. Check the Quick Format option. This will only take a few seconds to complete the formatting process.
Step 7. Press Start and then click OK to confirm the formatting operation on the partition.
Way 2. Use Disk Management
You can utilize Disk Management to format a new hard drive on Windows or to reformat an existing one. This Windows tool is also great for deleting disks and creating new partitions.
Follow the instructions to format your internal or external hard drive using Disk Management:
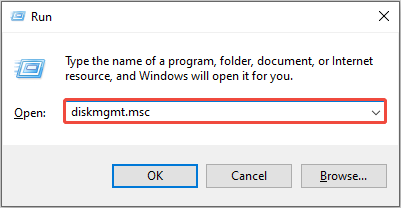
Step 1. Press Win + R together to open the Run command window.
Step 2. Type diskmgmt.msc and press Enter to access Disk Management.
Step 3. Make sure it’s connected to your PC if it’s an external drive. Right-click on the selected disk and choose Format.
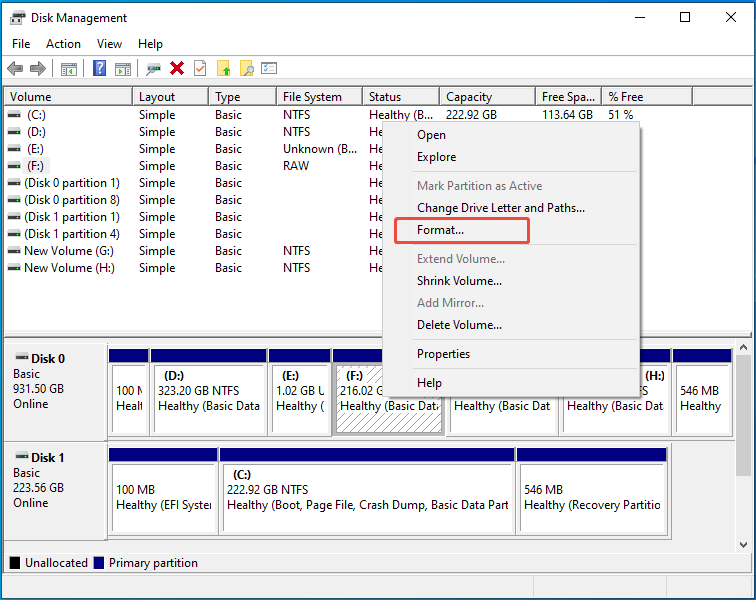
Step 4. Provide a name for the volume, select a file system, check the Perform a quick format option, and click OK.
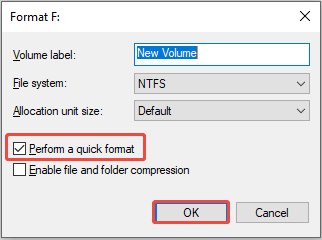
Step 5. Click OK in the pop-up window to finish the formatting operation.
Way 3. Use CMD
The DiskPart command-line tool for disk partitioning provides specific management capabilities for various computer drives, such as partitions, disks, virtual hard disks, and volumes. Utilizing DiskPart to format drives is an ideal option for advanced Windows users.
Just follow the steps outlined below carefully:
Step 1: Simultaneously press Win + R to open the Run window.
Step 2. Type diskpart in the window and then click OK.
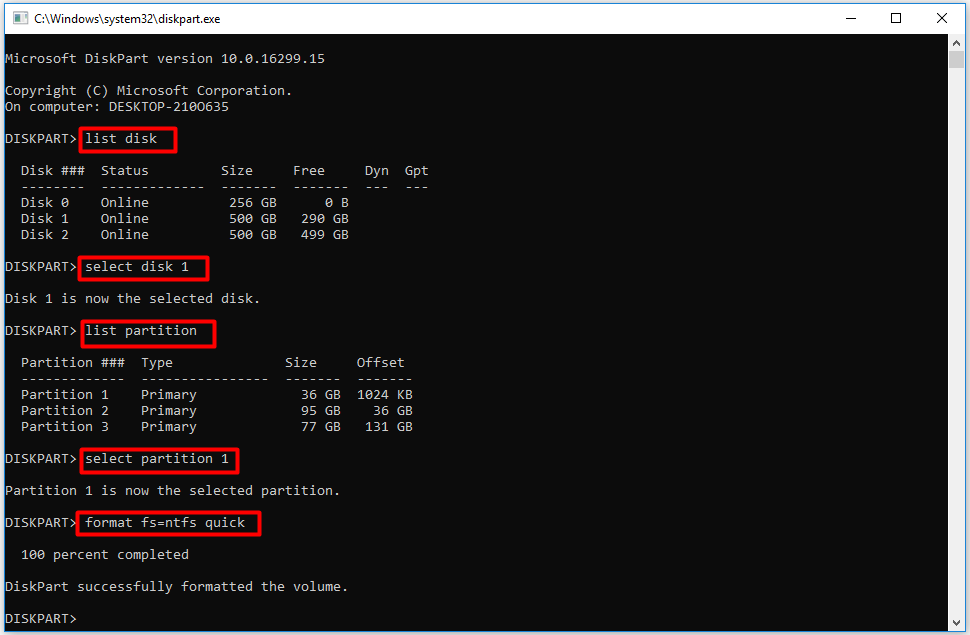
Step 3: Input a series of commands on the DiskPart screen. Press the Enter key after typing each command. The commands to be entered are as follows:
- list disk
- select disk X (X stands for the drive you want to format)
- list partition
- select partition X (X stands for the partition you want to format)
- format fs=ntfs quick
Way 4. Use PowerShell
PowerShell is a command-line shell and scripting language designed for managing system configurations and automating various tasks, among other applications.
To format a new hard drive on Windows 11/10 using PowerShell, follow these steps:
Step 1. Type PowerShell in the Windows search bar and choose Run as administrator.
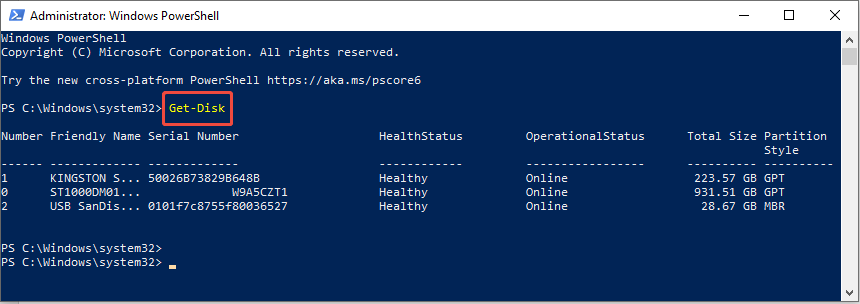
Step 2. Execute the Get-Disk cmdlet to view all connected drives.
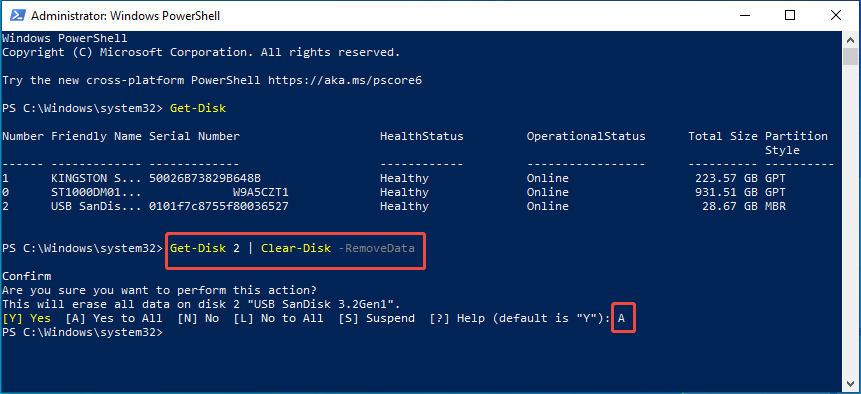
Step 3. To erase data before formatting unless the disk is new, run this cmdlet while replacing “2” with the appropriate number: Get-Disk 2 | Clear-Disk -RemoveData. Confirm by typing A and hitting Enter.
Step 4. Type this cmdlet to get the disk ready for formatting and press Enter: Initialize-Disk -Number 2 (substituting with your disk’s number).
Step 5. To format your drive, use this cmdlet: New-Partition -DiskNumber 2 -UseMaximumSize | Format-Volume -FileSystem NTFS -NewFileSystemLabel myDrive. Make sure to use the right number; you can change NTFS to another file system and myDrive to a different label.
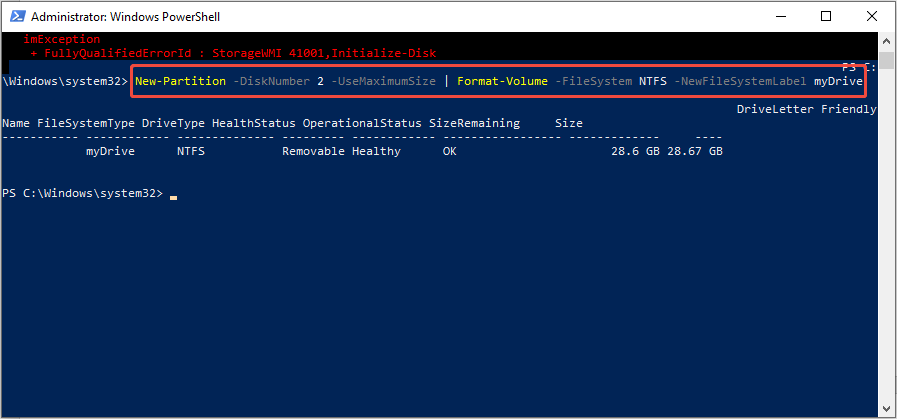
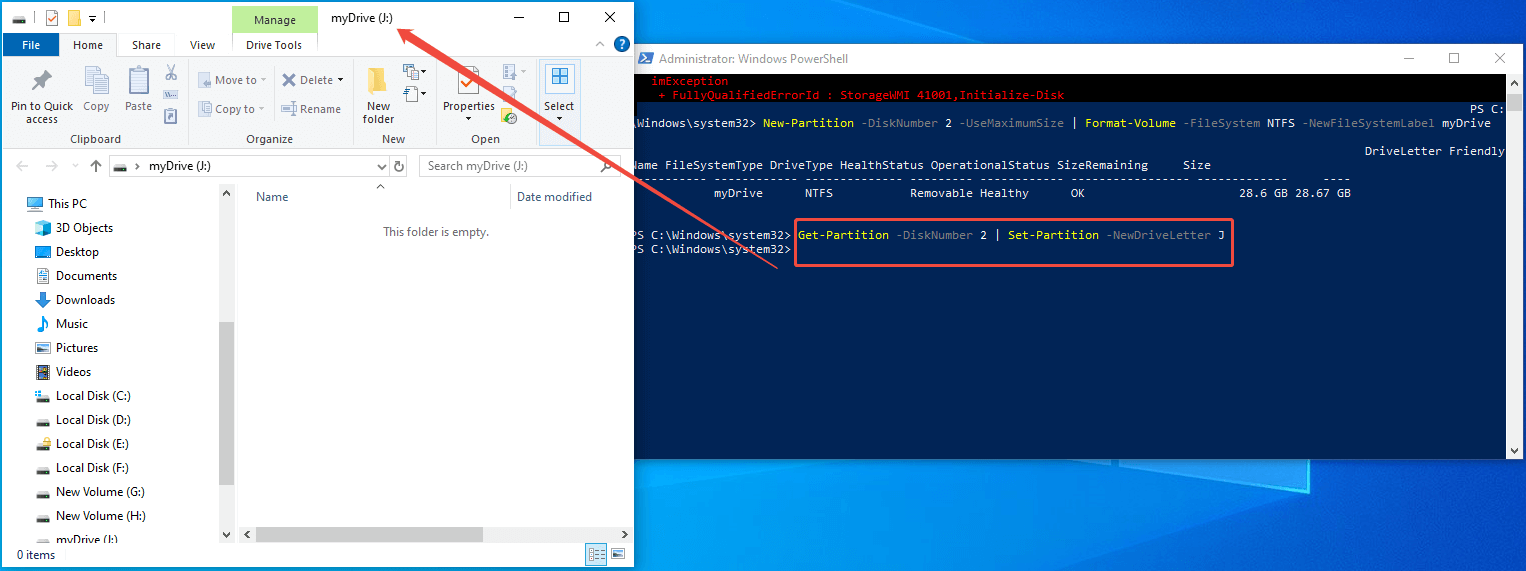
Step 6. Finally, run this cmdlet to assign a new drive letter: Get-Partition -DiskNumber 2 | Set-Partition -NewDriveLetter J (select any available letter).
Way 5. Use the CMD Convert Command
The Convert command available in Windows allows you to switch the file system of a volume from FAT or FAT32 to NTFS without the need to format the volume or risk losing any data. Here’s how to utilize it:
Step 1. Press the Windows + X keys to open the Power User menu and select Windows PowerShell (Admin) from the list.
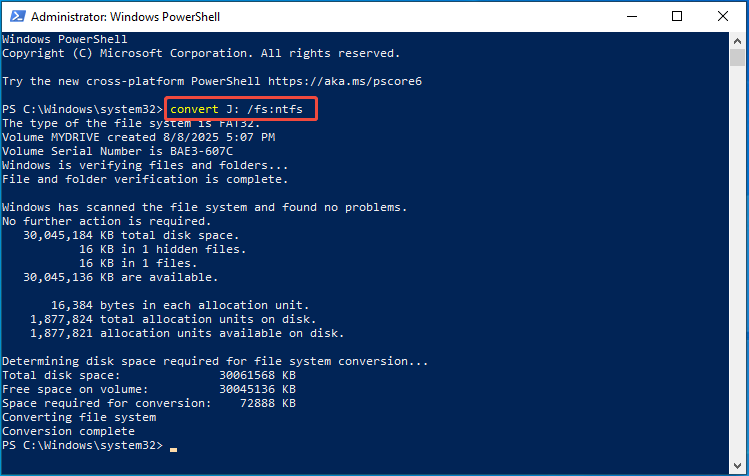
Step 2. Type the following command to change a FAT or FAT32 drive to NTFS: convert x: /fs:ntfs (ensure to replace ‘x:’ with the letter assigned to your hard drive)
Step 3. Press Enter to initiate the conversion process.
Way 6. Use MiniTool Partition Wizard
Formatting an internal or external hard drive is quite easy using MiniTool Partition Wizard. This is a professional partition management tool that offers powerful features like Data Backup, Disk Benchmark, and Partition Recovery, among others.
MiniTool Partition Wizard FreeClick to Download100%Clean & Safe
Here’s how to format a hard drive using MiniTool Partition Wizard.
Step 1: Open MiniTool Partition Wizard to access its main interface. Select the hard drive you wish to format and then click on the Format Partition option in the action panel.
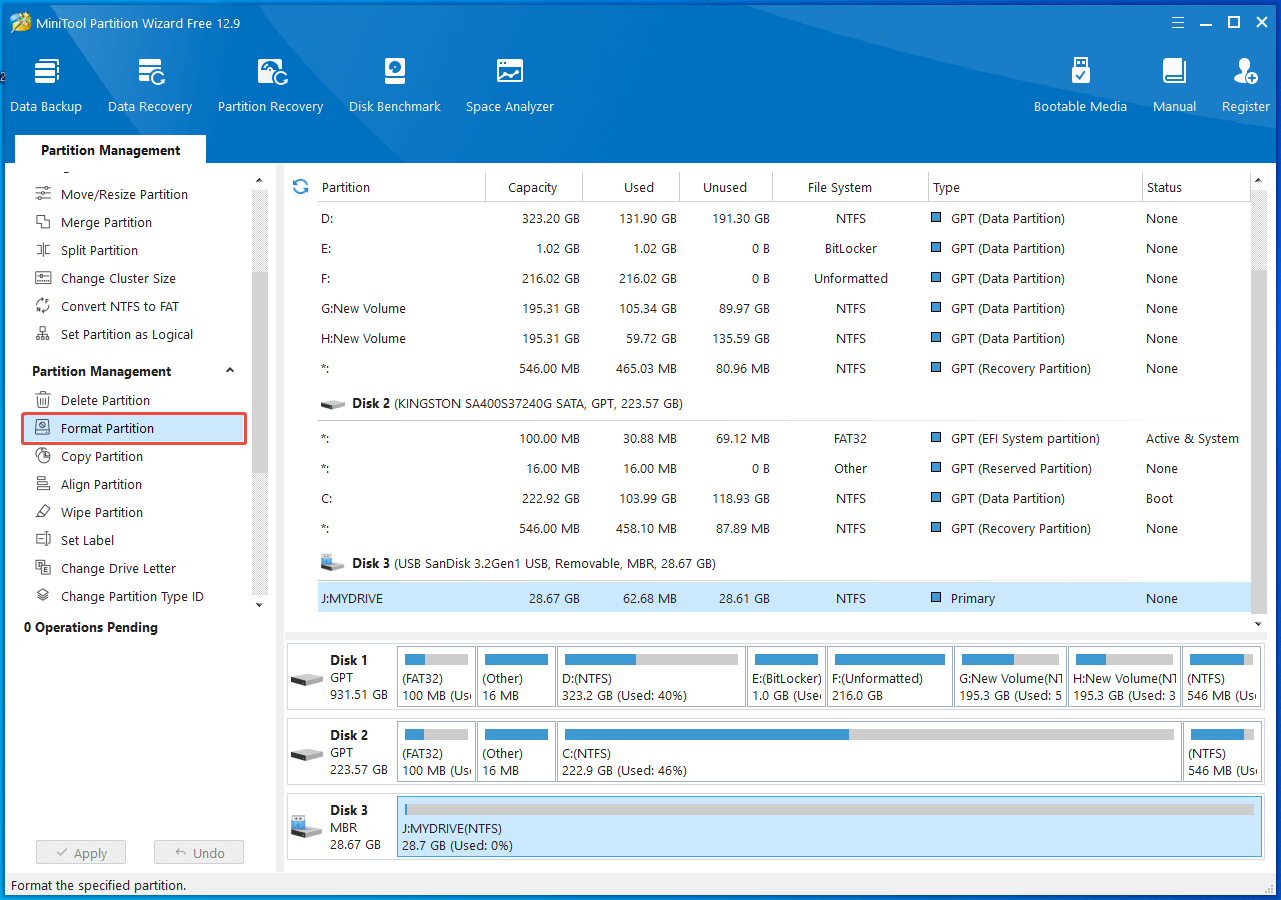
Step 2: After specifying the partition label and the desired file system, click the OK button to proceed with the process.
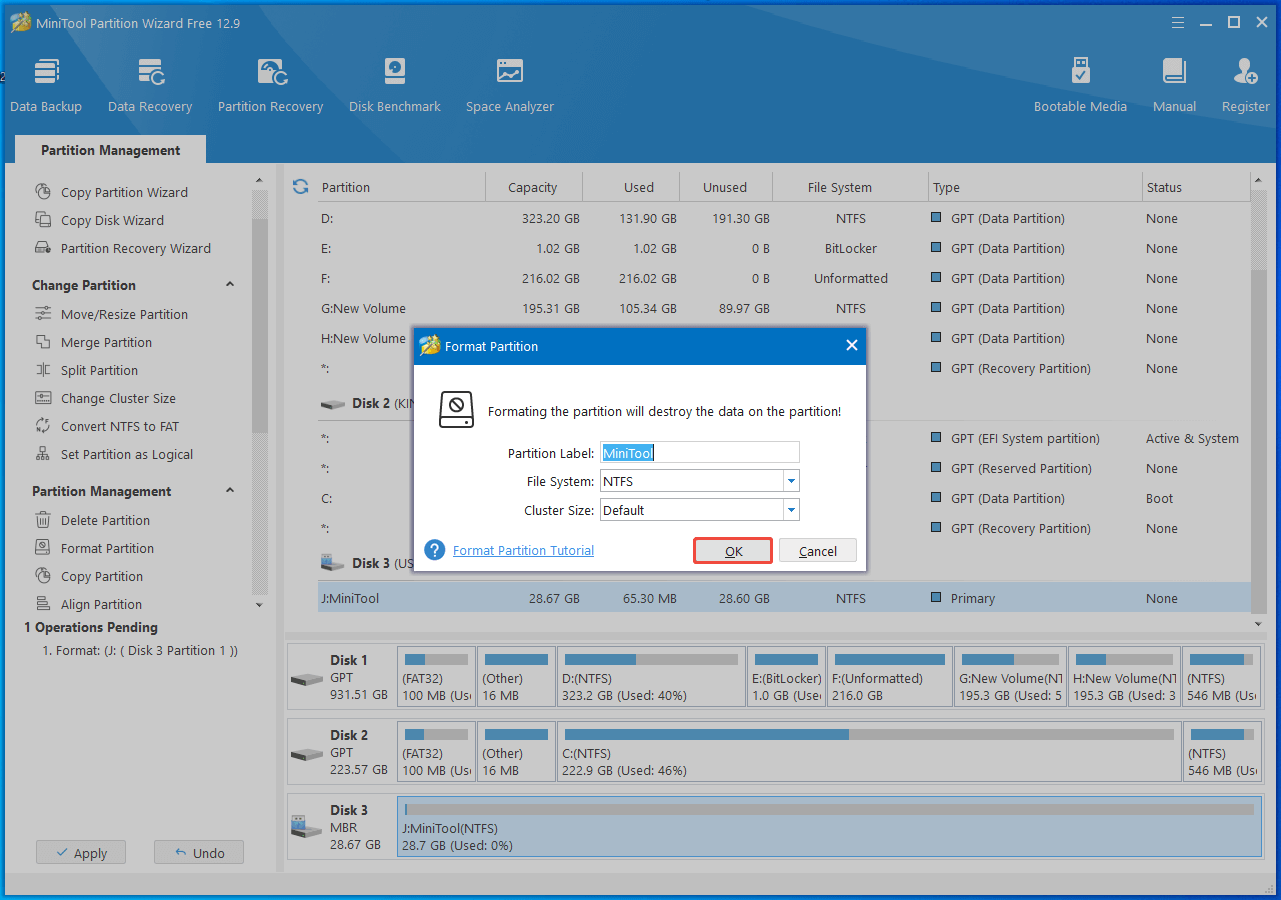
Step 3: Lastly, click Apply to carry out the pending operation.
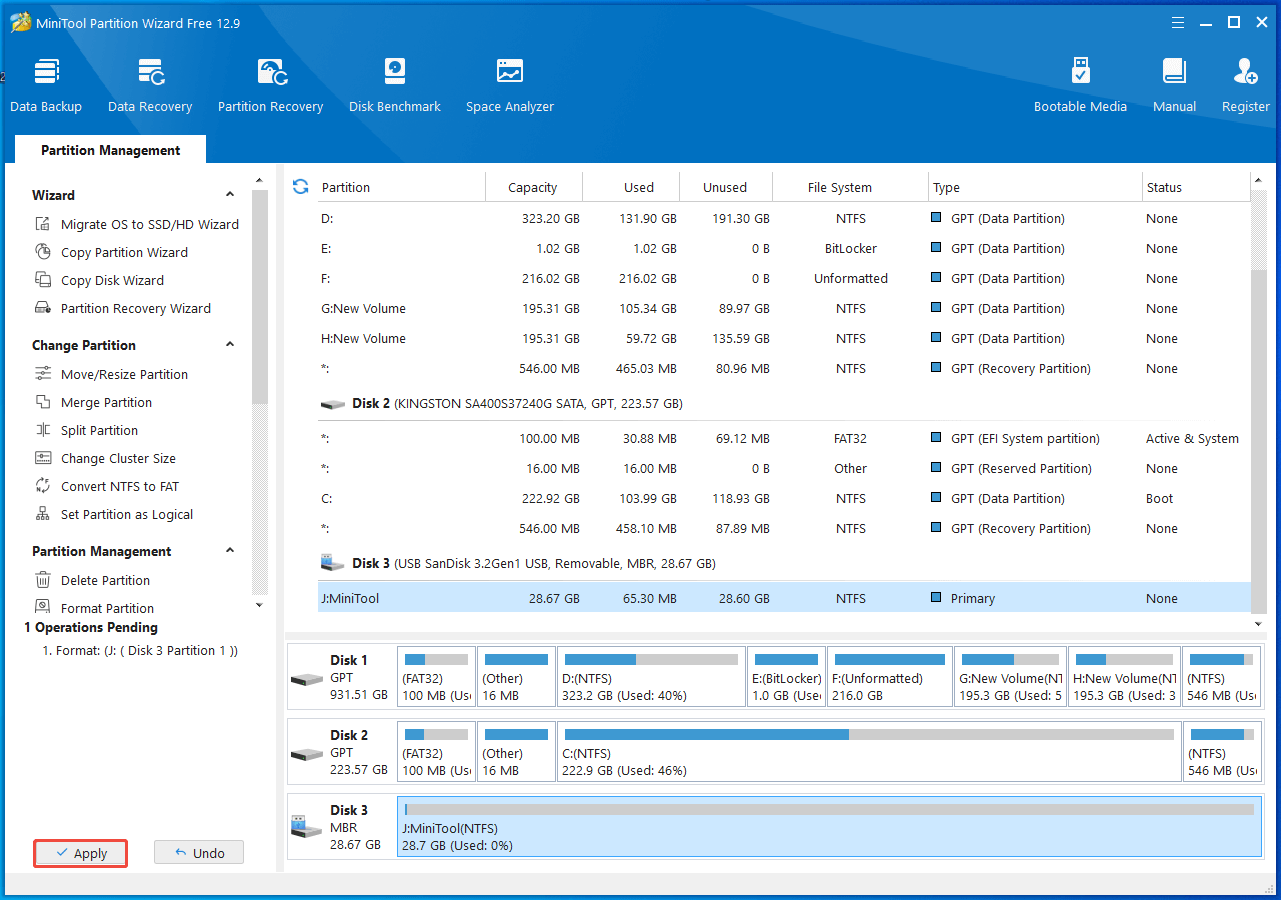
How to Recover Data from a Formatted Hard Drive
After formatting your external/internal hard drive, you can find that it is empty. To recover files from a formatted hard drive, MiniTool Power Data Recovery can assist.
What is MiniTool Power Data Recovery?
It is a specialized data recovery software intended for Windows users. Its purpose is to recover files from various storage devices, such as hard drives, SSDs, USB flash drives, SD cards, CDs/DVDs, and more.
What types of files can MiniTool Power Data Recovery recover?
It is capable of recovering a diverse array of file types, including documents, photos, videos, audio files, emails, archives, and others.
Is MiniTool Power Data Recovery free?
Not quite. The software provides a free edition, but it only permits the recovery of up to 1 GB of data without cost. If you only need to recover a handful of files, the free edition should suffice. However, for recovering more than 1 GB, you will have to upgrade MiniTool Power Data Recovery Free to access the additional files beyond the limit.
MiniTool Power Data Recovery FreeClick to Download100%Clean & Safe
Follow these steps below to recover your files from the hard drive.
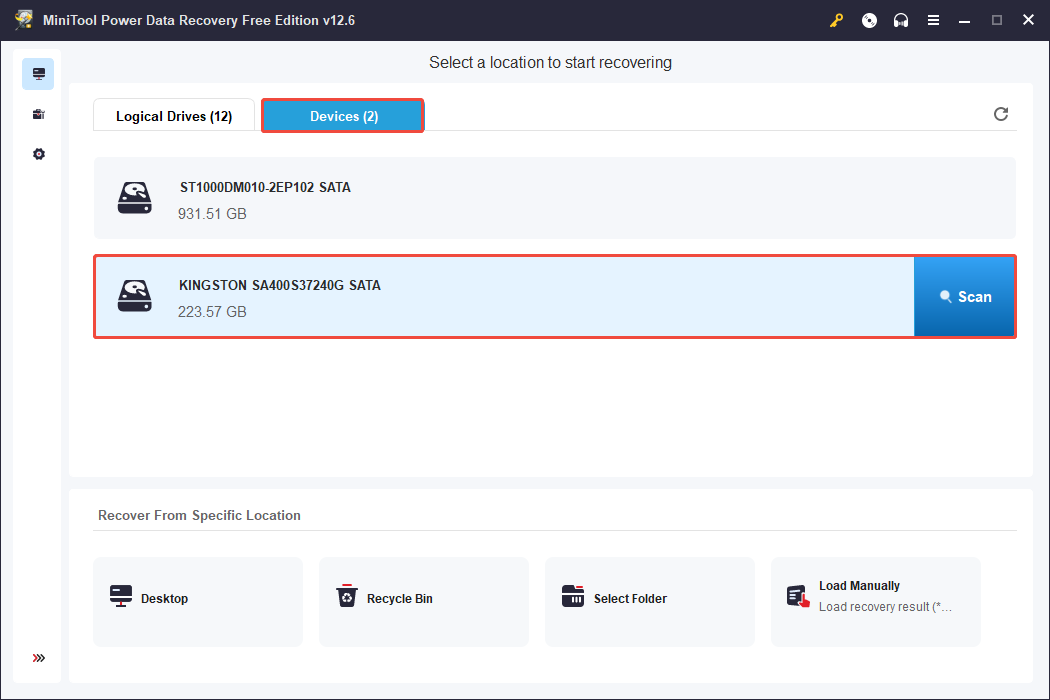
Step 1. Select the Internal/External Hard Drive to Scan
Double-click the MiniTool Power Data Recovery shortcut to launch the application. In the main interface, you should find the partitions for your external/internal hard drive displayed in the Logical Drives section.
To scan the whole hard drive, you can switch to the Devices tab. From there, select the drive from which you want to recover files and click Scan.
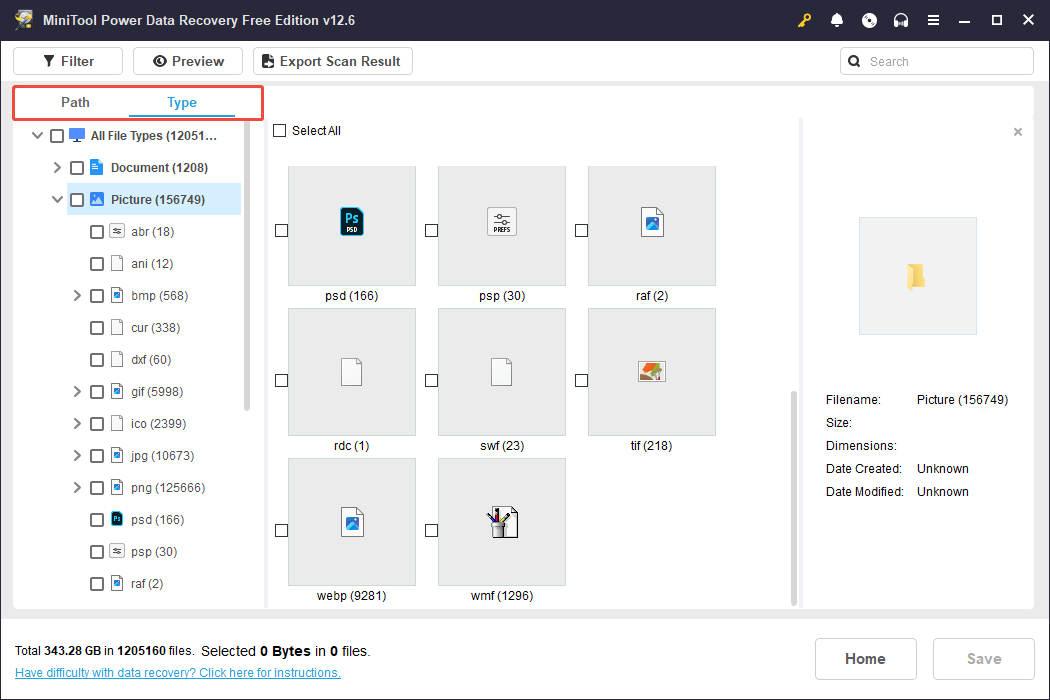
Step 2. Find and Preview Required Files
After the scan has finished, you can begin searching for the files you wish to restore. The MiniTool data recovery tool provides two ways to view files: Path and Type.
- In the Path view, you can expand directories to see your files organized by their original folder structure.
- In the Type view, you can explore your files categorized by their type and format. To recover photos, you should concentrate on the Picture section found under All File Types.
Moreover, the Filter and Search features can also help you find your files faster.
- Filter: Filter out unwanted files by file type, file modification date, file size, and file category.
- Search: Input keywords of your file name in the search box and press Enter to search for it.
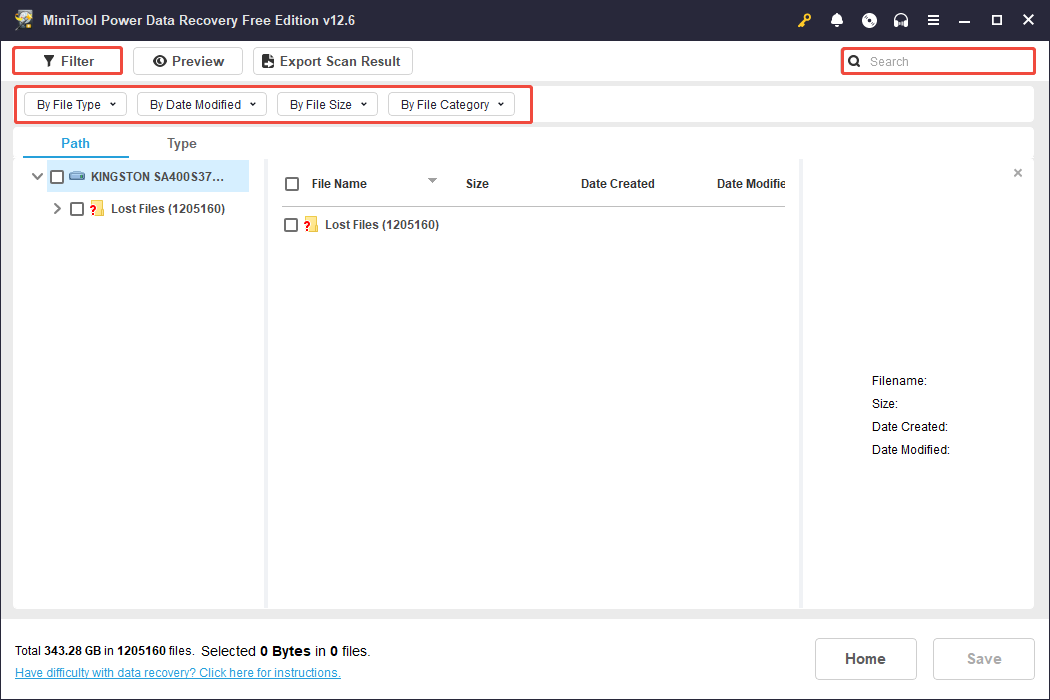
After locating a target file, you can double-click it to view its contents.
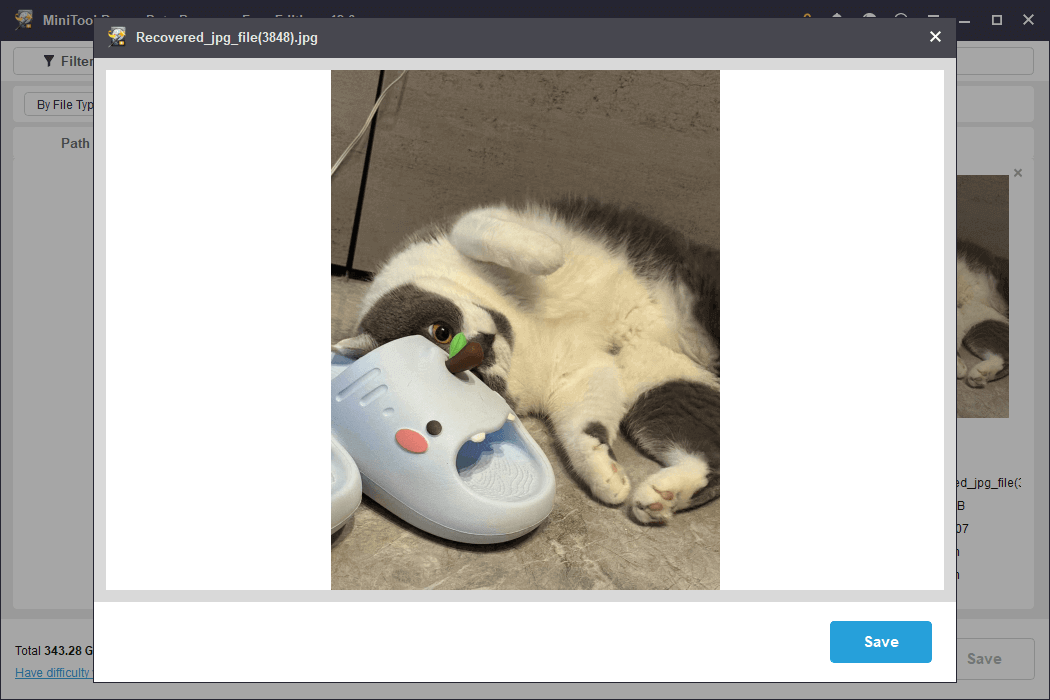
In the preview window, you have the option to click the Save button and select a destination to store the displayed image directly. Alternatively, you can follow the steps outlined below to save all the desired photos in one go.
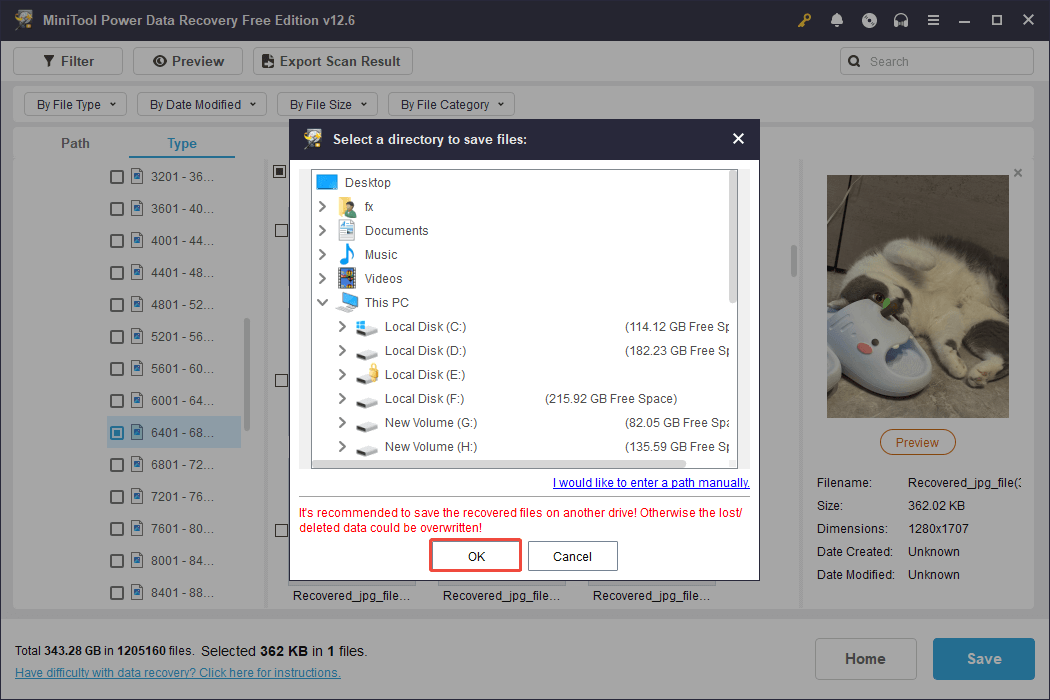
Step 3. Save Desired Files
Ensure that all the files you wish to recover are selected. Then, click the Save button located in the bottom right corner. In the pop-up window, choose a secure location and click OK to save them.
Wrap Up
Now you should know how to format a hard drive on Windows, whether it is internal or external. You can choose to format your drive from the File Explorer, Disk Management, use CMD, PowerShell, or a third-party formatter.
After formatting your hard drive, you can try using the professional and robust data recovery tool – MiniTool Power Data Recovery, to recover your formatted drive data.
If you encounter any problems or have any questions about MiniTool software, please send an email to the support team via [email protected].
Format a Hard Drive FAQs
Whether to format your hard drive as FAT32 or NTFS on Windows 11 depends on the storage size of your drive. FAT32 can handle volumes with a maximum size of 32 GB and files no larger than 4 GB. In contrast, NTFS supports volumes up to 256 TB and files that can reach 18 EB. Additionally, NTFS offers features like file compression, encryption, and access permissions.


User Comments :