“Disc” and “disk” are nearly identical in both spelling and pronunciation. This similarity frequently causes confusion among users about which term is appropriate in different contexts. This is a real case:
What’s the actual difference between “disc” and “disk”? I know they only differ by one letter, but I keep seeing “disc” for CDs and “disk” for hard drives. Is it just a British vs American spelling thing, or is there more to it? Any insights?reddit.com
In the following sections, we will provide a detailed explanation of what each term means and how they differ.
Part 1. Disc vs Disk: Definition
Disk and disc describe different types of storage media. Generally, “disc” refers to optical media, while “disk” refers to magnetic or solid-state storage devices.
What Is a Disc
A disc refers to an optical storage medium, such as the following:
- Compact Disc (CD): A round disc made of polycarbonate plastic that can store about 700 MB of data.
- Digital Versatile Disc (DVD): Similar in appearance to CDs but offers greater storage capacity. The capacity ranges from 4.7 GB (single‑layer) to 8.5 GB (dual‑layer), and up to 17 GB in rare double‑sided formats.
- Blu‑ray Disc: Developed to replace DVDs. It offers significantly larger capacity, ranging from 25 GB to 128 GB, making it suitable for storing high‑definition video files.

What Is a Disk
A disk typically means a magnetic or solid‑state storage medium, such as the following:
- Hard Disk (HDD): A traditional storage device that uses spinning magnetic platters to read and write data.
- Solid-state Drive (SSD): A storage device that uses flash memory chips instead of moving parts, offering much higher read and write speeds than HDDs.
After having a basic understanding of what discs and disks are, keep reading to explore the differences between them.
Part 2. Key Differences Between Disc and Disk
Because discs and disks are based on different designs and storage methods, they vary in storage capacity, read/write speed, writability, and other aspects. We will examine these differences one by one.
#1. Disc vs Disk Storage Mechanism
A disc stores data using optical technology. Information is encoded as tiny pits and lands on the reflective surface. Data is read and written by a laser beam that detects changes in reflection.
A hard disk stores data using magnetic technology. Data is recorded on spinning platters coated with magnetic material. The read/write head can magnetize a certain area to write data or sense the magnetic charge to read data.
An SSD uses flash memory to store data, and data is read electronically from memory cells.
#2. Disc vs Disk Capacity
As mentioned above, a disc usually stores data ranging from several hundred megabytes to about 128 GB of data. Optical discs are mainly used for sharing media and software, not for storing large amounts of data.
Modern hard drives and solid-state drives can typically store from hundreds of gigabytes to multiple terabytes of data. They are designed to store and manage large data.
#3. Disc vs Disk Speed
Optical storage media writing and reading speed:
- CD-ROM read and write speeds vary depending on the disc type. Early CD-ROM drives read data at approximately 150 KB/s (1× speed). Modern CD burners can achieve read speeds of up to 52×, which equals about 7.8 MB/s.
- For DVDs, the standard 1× speed equals 1.385 MB/s, while faster drives can reach around 22 MB/s at 16× speed.
- For Blu-ray discs, 1× speed is 4.5 MB/s, and advanced drives can achieve up to 72 MB/s at 16× speed.
The disc write speed is generally slightly lower than the read speed.
Disk read/write speed:
- HDDs generally provide read/write speeds of about 125 MB/s, depending on RPM.
- SSDs are faster than HDDs because they have no mechanical parts. Traditional SATA-based SSDs provide average read/write speeds of 500 – 550 MB/s. Premium SSD models can achieve speeds ranging from 2500 – 6000 MB/s, depending on interface and controller type.
#4. Disc vs Disk Writability
Different types of discs have distinct writability features:
- CD-ROMs (Compact Disc Read-Only Memory): cannot be written to.
- CD-R (Compact Disc Recordable), DVD-R, and BD-R: one-time writing and cannot be erased or modified.
- CD-RW (Compact Disc Rewritable), DVD-RW, and BD-RE: multiple writes, but the number of rewrite cycles is limited, ranging from hundreds to thousands.
However, unlike discs, HDDs and SSDs are designed for daily use and can handle many read/write cycles.
HDDs support almost unlimited read and write operations during their lifetime. SSDs can also be written many times, usually from a few thousand to tens of thousands of times.
#5. Disc vs Disk Usage Cases
Because optical discs and hard disks differ in speed, write performance, and durability, they are typically used in different scenarios.
Discs are primarily used for distributing music, movies, and software. They are also suitable for data archival or backup.
Disks are generally used for operating systems, applications, and daily file storage. They are also widely used in gaming due to higher speed and performance.
#6. Disc vs Disk Data Recovery Challenges
Generally speaking, data recovery from discs is more challenging than from disks. Once the surface of an optical disc is severely damaged, like scratches or cracks, recovery is usually very difficult.
HDD data recovery is relatively easier. Even if files are deleted, as long as they have not been overwritten by new data, they can often be restored using data recovery software.
SSD data recovery is also challenging due to the wear-leveling feature and the TRIM command, which can prevent deleted data from being recovered.
Overall, the table below summarizes the key differences between discs and disks across various dimensions:
| Disc | Disk | |
| Storage mechanism | Data is stored in the form of tiny pits on the optical disc. | HDD: Data is stored magnetically on spinning platters. SSD: Data is stored in flash memory cells. |
| Capacity | CD: 700 MB DVD: 4.7 – 17 GB Blu-ray: 25 – 128 GB | Hundreds of GB to several TB |
| Speed | Slower | Much faster |
| Writability | Read-only or limited | Continuous rewriting |
| Usage cases | Distribution, archival, or backup | Daily use |
| Data recovery difficulty | Difficult | Much easier |
How to Recover Files From a Disc
If you need to recover files from a disc, MiniTool Power Data Recovery can be a good choice.
This software supports almost all CD and DVD types, including CD-ROM, CD-R, CD-RW, DVD-ROM, DVD-R, and DVD-RW, and works well when discs are lightly scratched, corrupted, or partially unreadable.
Supported file types include documents, videos, photos, audio, and other files.
The Free Edition allows you to recover up to 1 GB of files at no cost. Download the free data recovery software and try it to see if your disc data can be restored.
MiniTool Power Data Recovery FreeClick to Download100%Clean & Safe
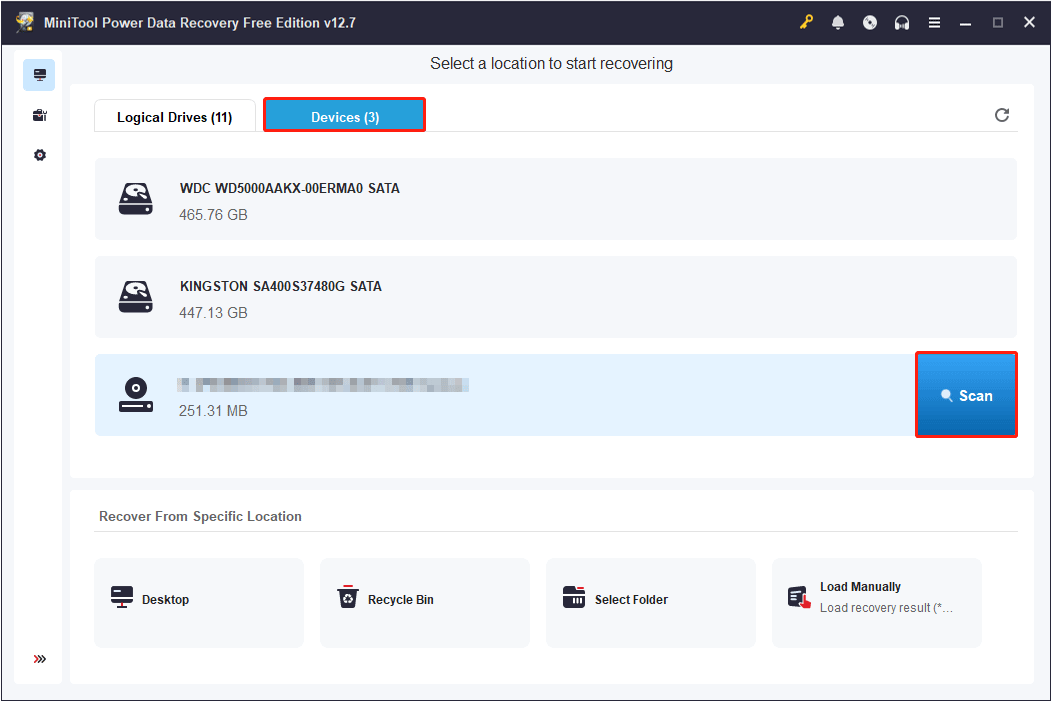
Step 1. Make sure your disc is properly connected to your computer.
Next, launch MiniTool Power Data Recovery to enter its main interface. Switch to the Devices tab, move your cursor to the target disc, and then click Scan.
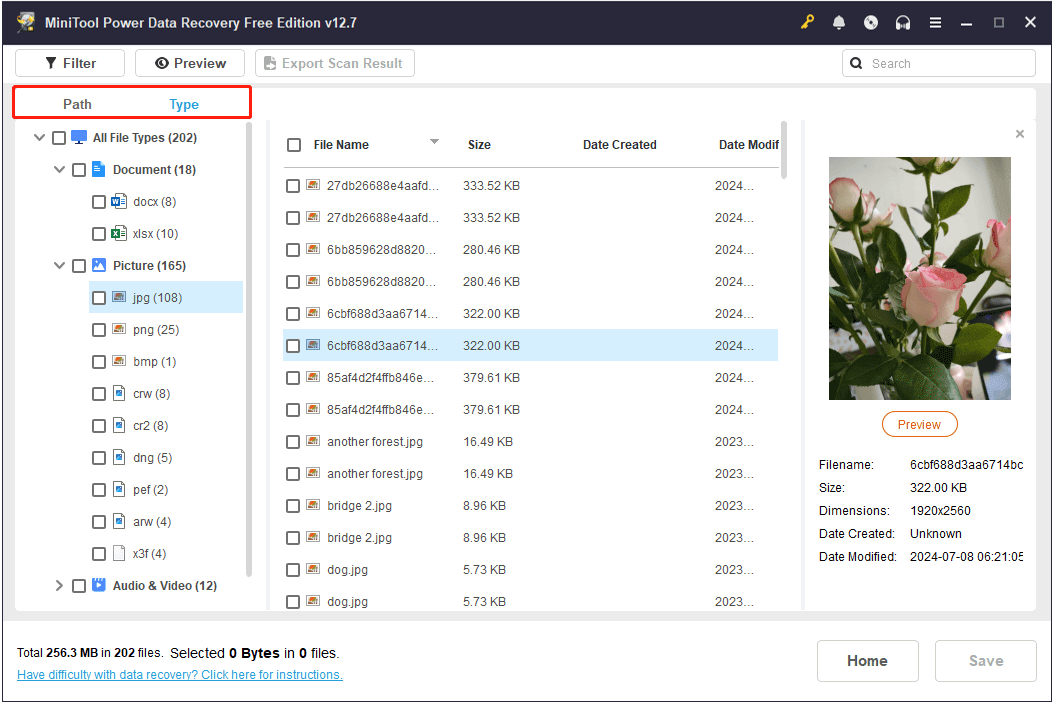
Step 2. After scanning, find your files under Path or Type.
- Path: If the folder structure is intact, files are listed in their original folders. You can open each folder to find the files you need. Tick the items once you find them.
- Type: If you only want certain kinds of files, this view is useful. Expand All File Types and then choose the specific type and format to locate what you need.
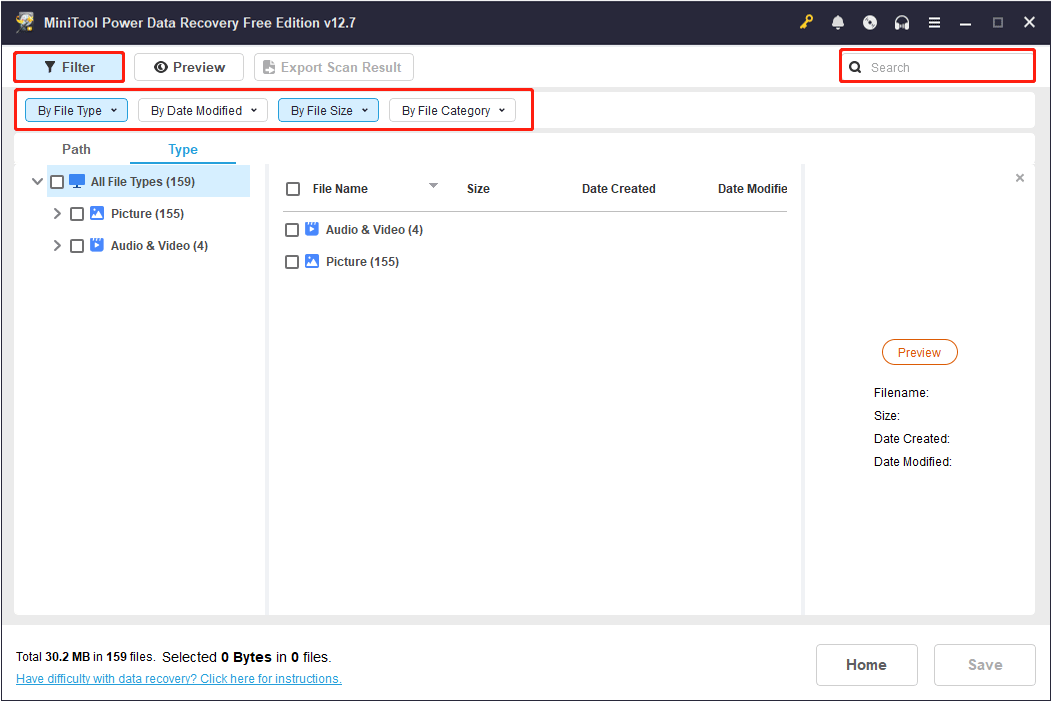
Moreover, the Filter and Search features can help you find files more accurately.
- Filter lets you set filtering conditions such as file type, modification date, file size, and file category to narrow down the results.
- Search lets you look for files by entering part or all of the file name.
Step 3. Double-click on each file to preview its content. Supported files to preview include videos, images, documents, videos, and more.
After confirming and checking all required files, click Save. In the new window, choose a safe location and click OK to store the recovered files.
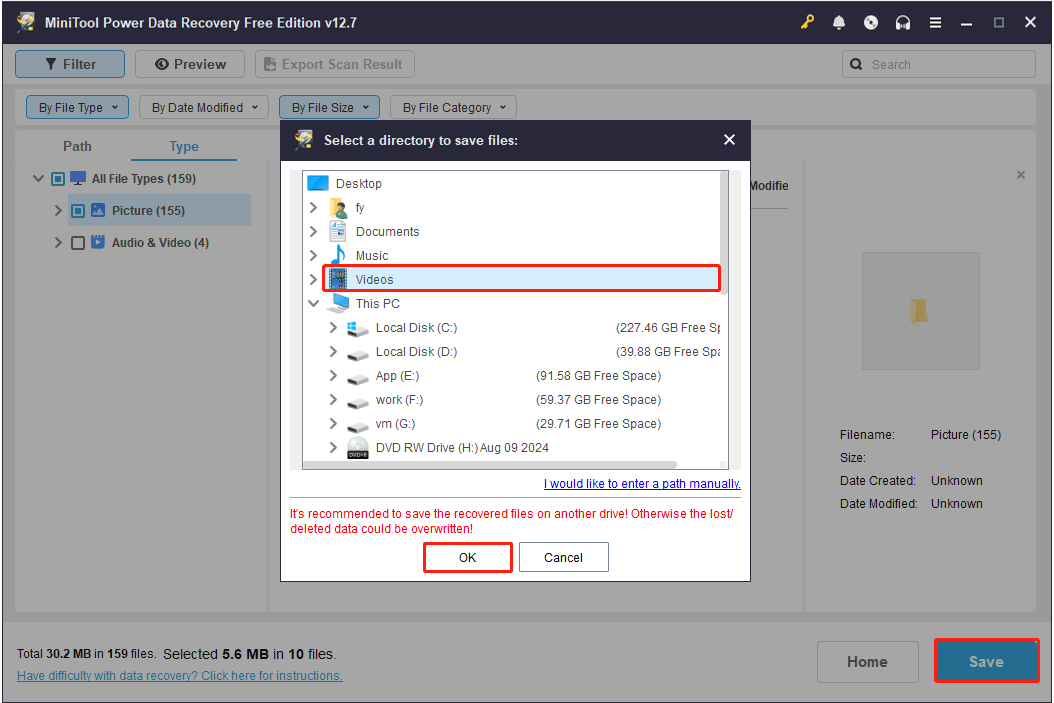
When the process ends, you can go to the selected location to view and use the recovered files.
How to Recover Files From a Disk
In addition to recovering files from CDs and DVDs, MiniTool Power Data Recovery also excels at restoring data from HDDs, SSDs, USB flash drives, SD cards, and many other types of storage media.
Whether your data is lost due to accidental deletion, disk formatting, partition loss, virus infection, or other reasons, this tool provides a secure data recovery solution.
The steps for restoring files from a disk are similar to those for a disc:
- Select the partition or disk to scan.
- Find your files by using Path, Type, Filter, and Search.
- Preview and save required files.
Part 3. Bottom Line
In summary, disc and disk are two similar but distinct concepts. A disc usually refers to optical media such as CDs or DVDs, while a disk refers to hard drives or solid-state drives.
They are manufactured with different materials, shapes, and purposes. This leads to great differences in data storage methods, typical capacity, read/write speed, and common usage scenarios.
If you lose data on a disc or disk, there is a chance to recover your files using MiniTool Power Data Recovery or through a reliable data recovery agency.
If you encounter any issues or need assistance while using MiniTool Power Data Recovery, please contact the technical support team at [email protected].



User Comments :